Summary
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to deliver a unique outcome, constrained by time, budget, and resources. Effective project management requires not only executing individual projects efficiently but also ensuring that the right projects are selected and prioritized.
Project Portfolio Management (PPM) plays a critical role in aligning projects with strategic objectives, optimizing resource use, balancing risks, and maximizing business value.
Supporting functions such as program management, resource management, and demand management are essential to assess feasibility, manage capacity, and translate business needs into actionable initiatives. Due to limited resources and conflicting priorities, organizations must make benefit-driven decisions, continuously reassessing project value and alignment.
PRINCE2 provides a structured approach with clear roles and emphasizes continuous business justification.
Ultimately, successful project execution depends on the integration of governance, strategic alignment, and informed decision-making across all levels of the portfolio.
Project Portfolio Management Vs. Project Management
It is generally accepted that a project is a temporary effort undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. It has a clear beginning and end, and it’s usually constrained by time, budget, scope, and resources.

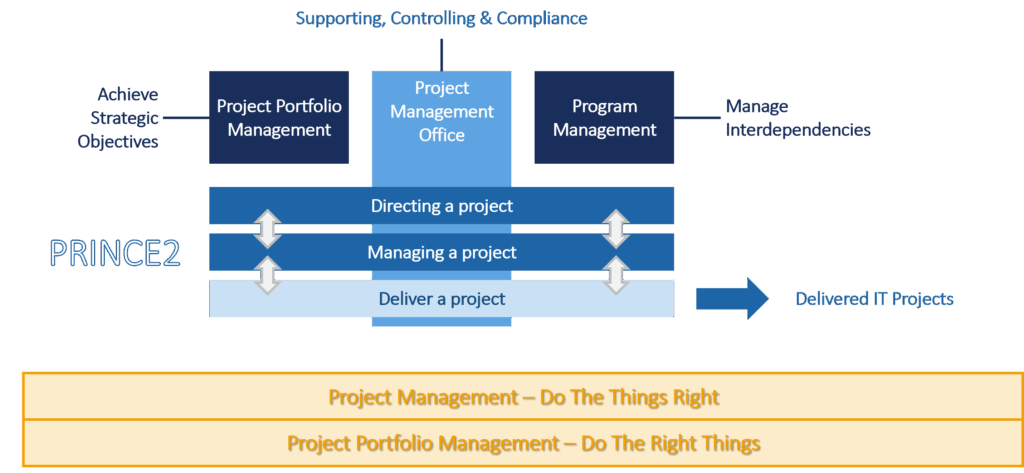
PRINCE2 differentiates 3 layers:
- Directing a project
The Project Board provides overall direction and decision-making throughout the project. - Managing a project
The Project Manager runs the day-to-day management of the project. - Delivering a project
This is the actual creation of deliverables under the direction of the Project Manager
Projects are related to:
- Project Portfolio Management
Project portfolio management is the strategic management of a group of projects and programs (owned by an organization) to ensure they collectively achieve an organization’s objectives, optimize resource use, and balance risks and returns. - Project Management Office
The project management office is a supporting function for project management. - Program Management
Program management is the coordinated management of multiple related projects (dependencies), aligned to achieve strategic objectives and deliver benefits that wouldn’t be realized if the projects were conducted separately.

Not every project can be realized
- Resource and budget limitations mean we cannot execute all proposed projects.
We must place our limited amount of chips on the right squares! - Trade-offs are necessary.
Projects may have conflicting objectives.
- Some projects support different or even opposing strategic goals.
- Alignment with overall business priorities is key.
Projects vary in value and urgency.
- Certain projects are critical and must be delivered to ensure business continuity.
- Others are less urgent or can be postponed
Decision-Making should be benefit-driven.
- Each project’s expected value should be weighed against its
- Risks (threats and opportunities)
- Required resources
- Duration
- Budget impact
It’s about making smart choices
- We must accept that we can’t satisfy every demand.
- Our limited resources must be allocated where they create the most impact.
Process Context
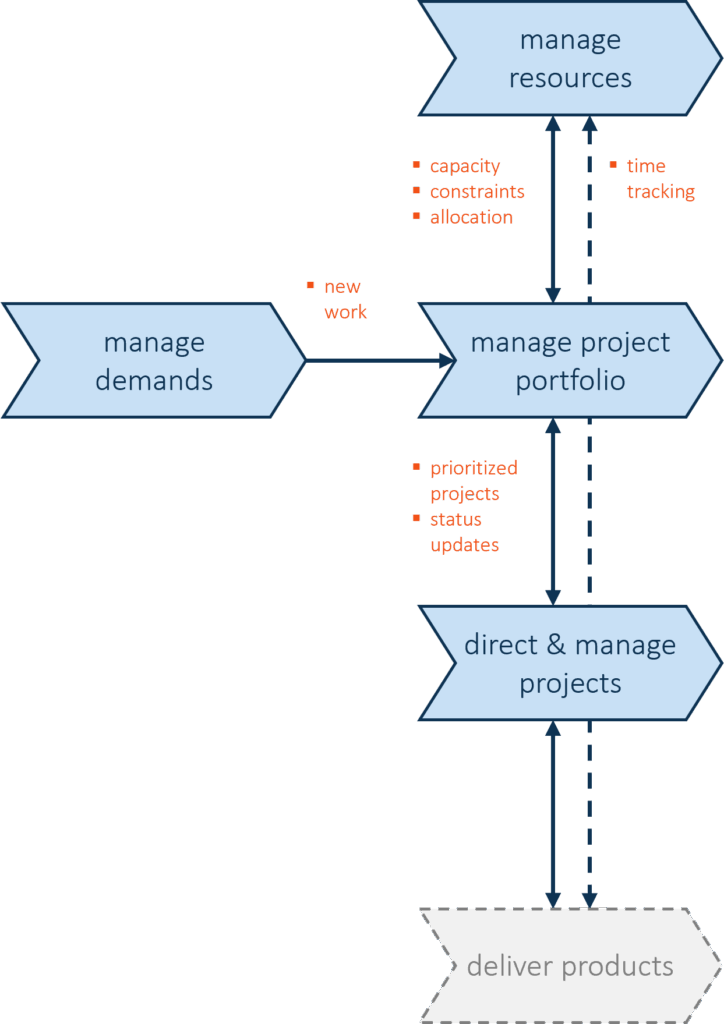
Project management, project portfolio management, resource management, and demand management are interconnected, each playing a distinct role in ensuring successful project execution and strategic alignment.
Demand Management is responsible to capturing, evaluate, and (pre-) prioritize business needs and transform them into specified demands. It relies on resource management to validate capacity to meet new demands. it feeds into project portfolio management , which decides which demands should become active projects.
Resource Management ensures the allocation and optimization of people (tools, materials) across projects. It depends on project portfolio management for prioritized project lists. It relies on demand management to anticipate future resource needs. It depends on project management for resource assignments and usage feedback.
Project Portfolio Management selects, prioritize, and oversees a portfolio of projects to align it with business goals. It depends on demand management to identify potential projects. It relies on resource management to assess feasibility and resource capacity. It requires project management to provide delivery updates and ensure execution aligns with strategy.
Project Management focuses on the execution of individual projects. It relies on resource availability (provided by resource management)and project prioritization (provided by portfolio management).
Functions / Purpose
Project Portfolio Management helps organizations “do the right projects” rather than just “do projects right.” It ensures that the collective efforts of all projects drive organizational success. The purpose is:
Strategic Alignment ensures that projects support the organization’s long-term goals and priorities (by selecting the right projects).
Resource Optimization helps allocate resources (people, budget, time) effectively across multiple projects.
Risk Management identifies and balances risks across the portfolio, not just within individual projects.
Performance Monitoring tracks project performance and progress at a portfolio level to ensure expected benefits are being realized.
Informed Decision-Making provides executives and stakeholders with data and insights to prioritize or terminate projects based on value, cost, risk, and strategic fit.
Maximizing Business Value focuses investment on projects that offer the highest return on investment and overall value to the organization.
Governance and Control establishes clear processes, standards, and accountability for project selection, funding, and execution.
Introduction Of Project Portfolio Items
To setup a Project Portfolio Management you can choose project portfolio items. A project portfolio item is one of the following
- Specified Demand
- Project Brief
- Project Initiation Document
- Stage Plan (request to release next stage)
For each of items above the project portfolio manager takes one of the following decisions:
- Reject
- Approve (= continue with project)
- Set on hold (= stop project, resume project later)
- Close regularly
- Close prematurely
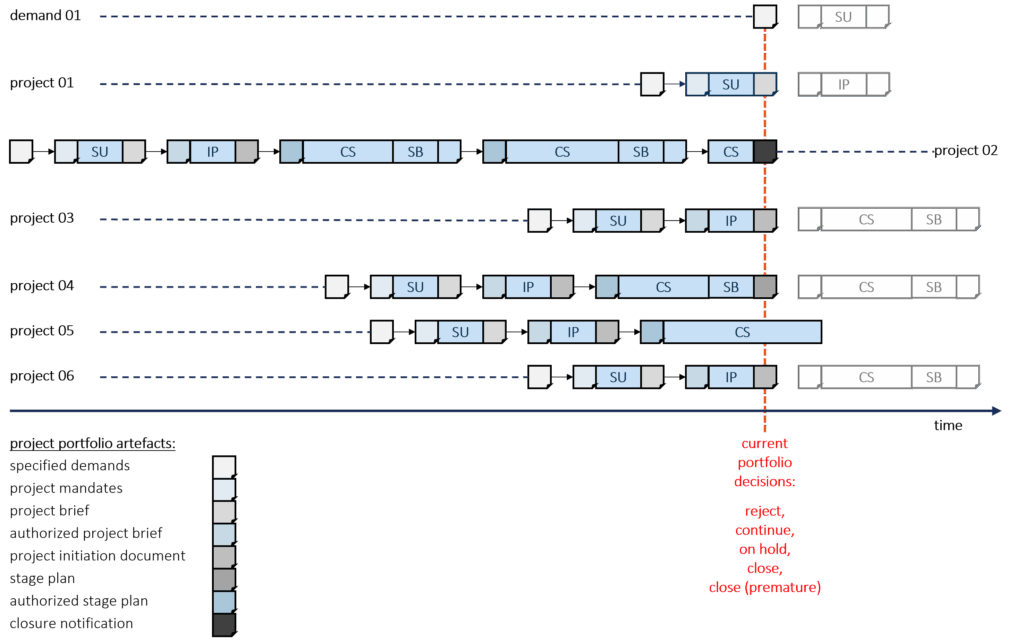
The decisions are normally taken in the project portfolio board. Among others the decisions are taken based on the following criteria:
- existing constraints like available budget and available capacity of human resources
- expected benefits (monetary / nonmonetary)
- risk evaluation (threads / opportunities)
- fit to strategic needs
The Resource Capacity Constraint
The graph below shows an example of the resource capacity constraints.
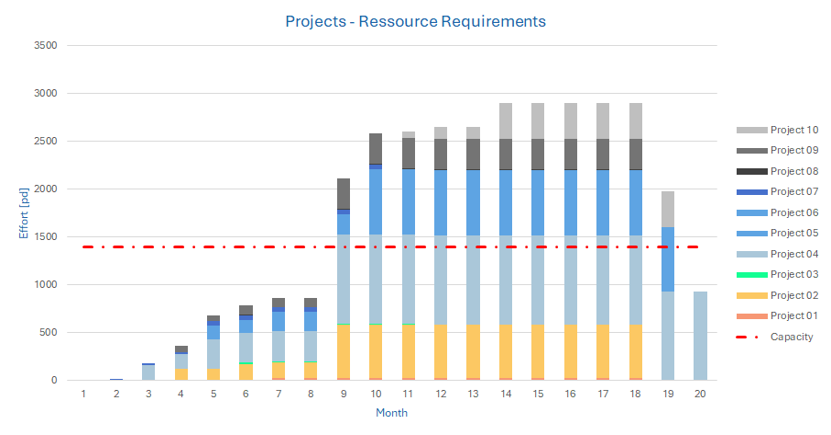
In month 9 the total required resources exceeds the resource capacity limit.
Resource conflicts lead to
- overburden & multitasking
- poor quality
- Delays in project delivery
Portfolio management need to consider resource constraints when new projects are release (same applies to budget and timeline constraints).
Resource management needs to be implemented to a suitable maturity level
0 – nothing
1 – planning only
2 – planning & allocation
3 – planning, allocation, and tracking
4 – …on cost unit or work package level
5 – forecasting
A similar approach can be used to identify budget constraints.
Interface Project Management & Project Portfolio Management
When arriving a stage gate the portfolio management is involved to select the “right” portfolio items to maximize the business value.
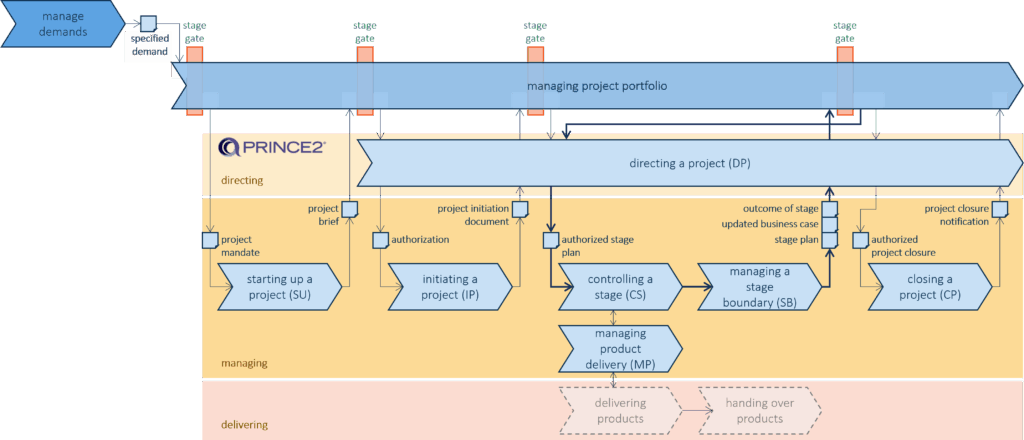
Following parameters are considered:
- Scope
- Quality
- Timeline
- Resources
- Cost (Purchases)
- Benefit
- Risks / Issues
